Scalar Fields
A scalar field assigns a value to every position in space. The space could be a 1D line, 2D surface, 3D volume, or higher dimensional spaces. Examples include the electric potential along a wire \( V(x) \), the height of a mountain range \( h(x,y) \) or the density throughout an object \( \rho(x,y,z) \).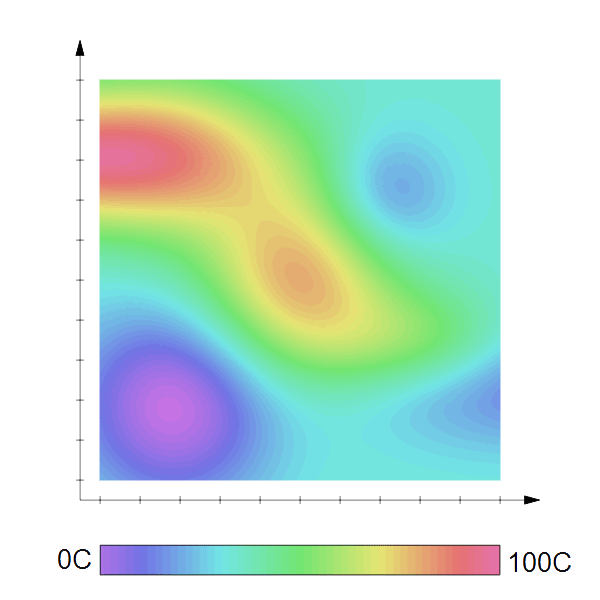
A 2D scalar field showing the temperature distribution in a sheet of metal. The colour represents the temperature.