Vector Fields
A vector field assigns not only a value, but a direction to every position in space. Examples include the flow of heat on a sheet of metal \( \vec{J}(x,y) \) or the velocity of water within a river \( \vec{v}(x,y,z) \).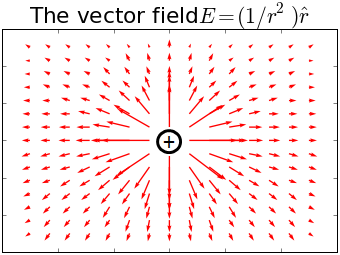
The electric field due to a positive point charge.